|
|
|
Aftercare
|
|
|
|
|
|
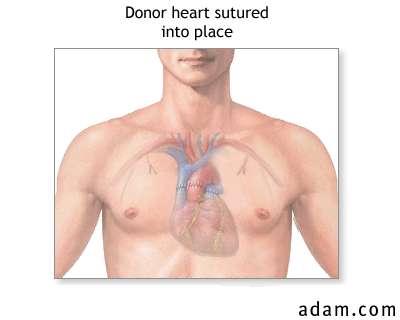
Heart transplant prolongs the life of a patient who otherwise would die. About 80% of heart transplants are alive two years after the operation. The main problem, as with other transplants, is graft rejection. If rejection can be controlled, then survival can be increased up to 10 years or more. Immunosuppressive drugs must be taken indefinitely. Relatively normal activities can resume as soon as the patient feels well enough and after consulting with his or her doctor. However, vigorous physical activities should be avoided.
The major problems are the same all major organ transplants face:- a shortage of donor hearts
- rejection of the transplanted heart
- cost of the surgery and post-operative care, including immunosuppressive drugs
|
|

|
The information provided herein should not be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Copyright 2000 adam.com, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
|
|